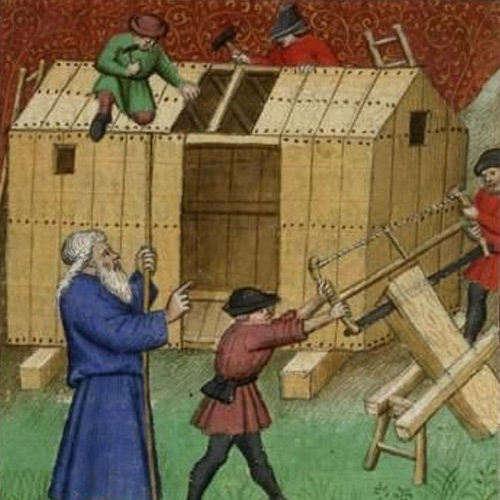

Carpenters from medieval times were highly skilled workers. They cut timber to make fences, wooden beams, planks, windows and doors, and furniture. Carpenters produced most items used during daily life.
To become a carpenter, a man had to usually join a guild as an apprentice and learn the craft, which included knowledge of math, woodworking, and tools.
The best carpenters were sometimes employed by Kings and nobles and retained as specialists. In this article, we take a look at how carpenters came to be and what they daily life was like in the middle ages.
History of Carpenters
Wood is one of humankind’s oldest building materials used throughout the Stone Age to the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. Although relatively little information about carpentry is available from prehistory, there’s a surviving complete architectural text, the Roman architect’s Vitruvius‘ ten books collectively titled De architectura, written for emperor Caesar Augustus between 30 and 15 BC. The treaty discusses some carpentry.
The majority of Britain towns were often founded near the fortifications the carpenters had built for feudal lords, monasteries, or the ruins of antique cities from which they could take building materials.
Carpentry guilds became possible when towns began to stabilize and expand around the year 900, although guilds’ proper organization didn’t happen until the 12th Century. In formal training, a carpenter began as an apprentice, then became a journeyman, and with enough experience and competency, they could eventually attain the status of a master carpenter. This progression path is kept today.

Medieval Carpenter Tools
Carpenters in the Middle Ages created useful items that included furniture, tools and utensils, wagons, and even homes.
Among their main tools were sanders used to smooth the wood, miters used to create joints, and routers to make grooves. According to G.R. Halstead’s ‘European woodworking tools 600-1660 C.E.’ booklet, a medieval carpenter’s toolbox consisted of:
- Hatchet, twybill, felling axe & broad axe
- Gimlet, auger & brace
- Compass, square & ruler
- Grooving iron & twyvette
- Saw
- Adze
- Plane
- Chisel & gouge
- Awl & marking gauge
- Crowbar
- Hammer
Additionally, carpenters used whetstones to sharpen their tools. Some medieval tools have been found in the Mästermyr chest (a 12th century Viking tool chest from Sweden) and in the wreck of the Mary Rose and Vasa.
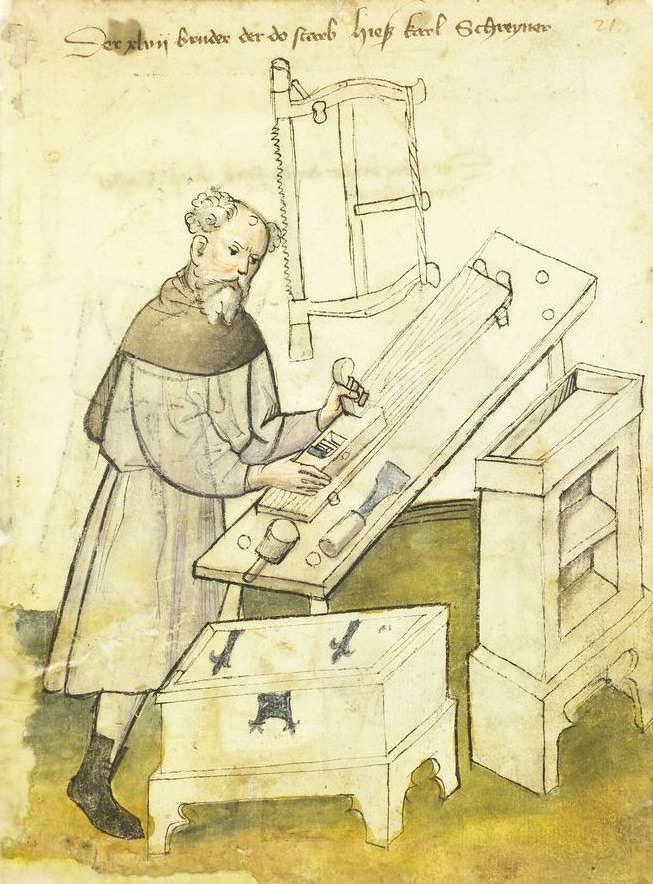

Carpenter Guilds
Carpenter guilds originated to promote fair competition and agree on some basic rules governing their trade.
Guilds could oversee their members’ practices and be able to impose fines on those found in violation of the rules. They would also care for any member who fell sick, arrange burials and take care of the less prosperous widows and orphans, and support their towns, often building schools and churches.
Carpentry apprenticeships were highly valued, and families sometimes had to pay a master a large sum of money to enroll their son. It was only after five to nine years that an apprentice could become a journeyman. Only after showing proof of his technical competence (the “masterpiece“) could he achieve the status of master and set up his own workshop.
Books about Medieval Life
More Medieval Occupations

Medieval Minstrel
Medieval minstrels sang, played musical instruments, and told engaging stories. Here’s what life was like for a minstrel in the Middle Ages.

Medieval Miller
Millers were some of the most important tradesmen in the Middle Ages. Learn more about this medieval profession and how millers lived.

Medieval Butcher
Middle Ages butchers prepared meat, fish, and fowl for the people in a castle or a city. They sometimes had stalls in a marketplace.

Medieval Wheelwright
Medieval candlemakers made candles from materials such as fat, tallow and beeswax.
Medieval Shoemaker
Medieval candlemakers made candles from materials such as fat, tallow and beeswax.

Medieval Shipwrights and Shipmaking
Being a sailor in the middle ages meant living a lonely and difficult life, as they would often set sail for months or even a year at a time.








