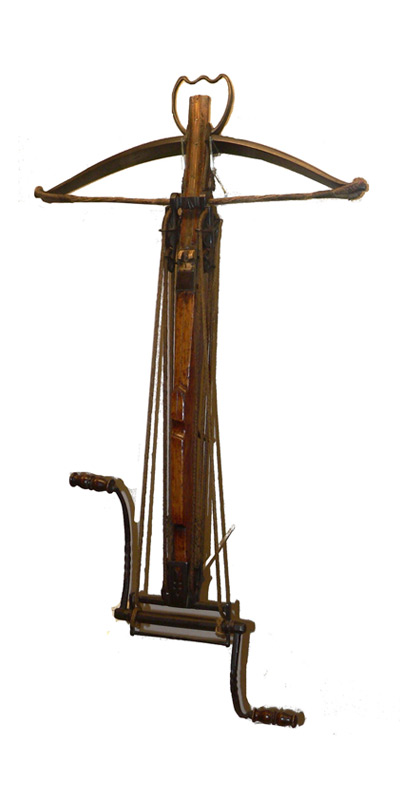
The crossbow is a type of elastic ranged weapon that consists of a bow-like assembly or prod mounted horizontally on a mainframe or tiller. A crossbow shoots bolts or quarrels.
Because crossbows use a locking mechanism, crossbowmen could handle stronger draw weight and hold for longer with significantly less physical strain, providing them with better precision.
The arrow-like projectiles of a crossbow are called bolts. Shorter than arrows, they can be several times heavier. They were fitted with various heads, some with sickle-shaped heads to cut rope or rigging, and others with a four-sided point called a quarrel.
History of the Crossbow
Crossbows played a significant role in the warfare of Medieval Europe and East Asia.
The first crossbows were invented in ancient China and cause a major shift in projectile weaponry’s role. Unlike the bow, which required considerable training, physical strength, and expertise, the crossbow was simple to use, cheap to make, and physically undemanding. It was the perfect weapon for large numbers of untrained conscript soldiers.
A small body of evidence points out that the ancient European crossbow was primarily a hunting tool or minor siege weapon. The earliest European crossbow designs featured a transverse slot in the top surface of the frame. A vertical rod thrust up through a hole in the bottom of the notch forced the string out. A later design implemented a rolling cylindrical pawl called a nut held in place by wood, ivory, or metal to retain the string.
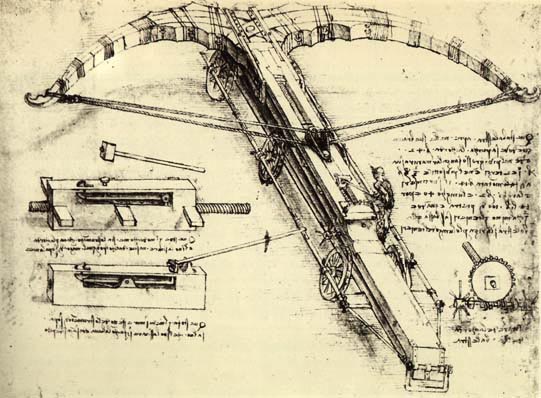
Crossbows were used at the battle of Hastings in 1066, and by the 12th century, they had become a common battlefield weapon. By the 13th century, European crossbows used winches and various spanning mechanisms such as winch pulleys, cord pulleys, gaffles, cranequins, and screws.
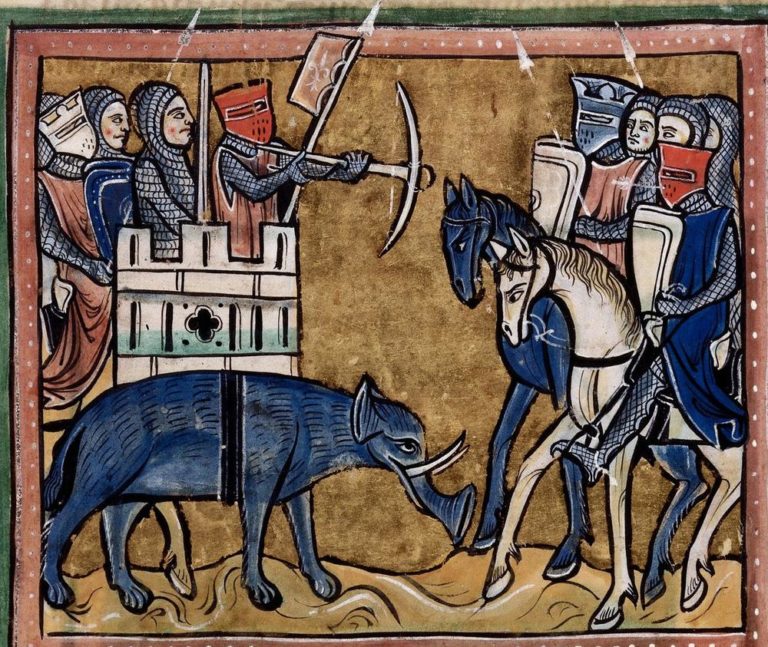

Types of Crossbows
Gastraphetes
This type of crossbow was described by Heron of Alexandria in the 1st century AD, who believed it to be the catapult’s forerunner. The weapon was powered by a composite bow and cocked by resting the stomach in a cavity at the rear of the stock and pressing it down. Heron identifies the gastraphetes as the forerunner of the catapult, which means it was invented some time before 420 BC. According to E. W. Marsden, it was invented in 399 BC by a team of craftsmen assembled by Dionysius I of Syracuse.

Pistol Crossbow
These were smaller crossbows that could be shot from under the arm. Pistol crossbows are weaker than regular ones, because their arm draw is shorter. Later, stocks of the shape that would then be used for firearms were added.
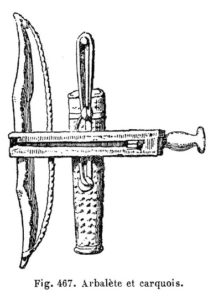
Arbalest
The arbalest was a late variation of the crossbow first used in Europe during the 12th century. Much larger in size, the arbalest had a steel prod and greater force. The strongest windlass-pulled arbalests could have up to 22 kN (5000 lbf) of force and be accurate up to 100 m. A skilled arbalestier could loose about two bolds per minute.
The word arbalest originates from the Roman name arcuballista (a combination of the words bow and missile-throwing engine), which was used for crossbows and types of artillery.
Using Crossbows
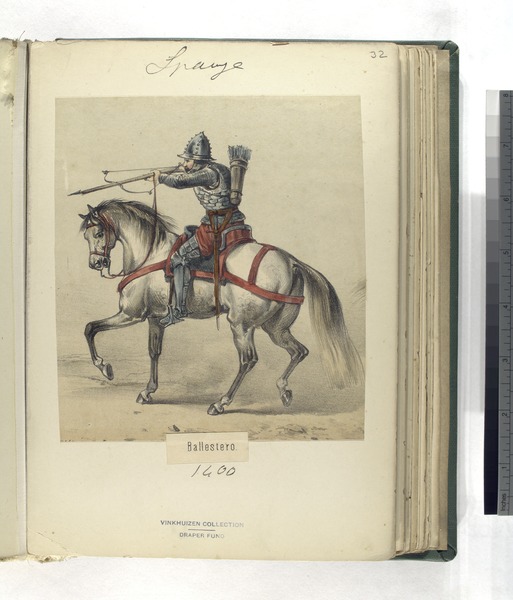

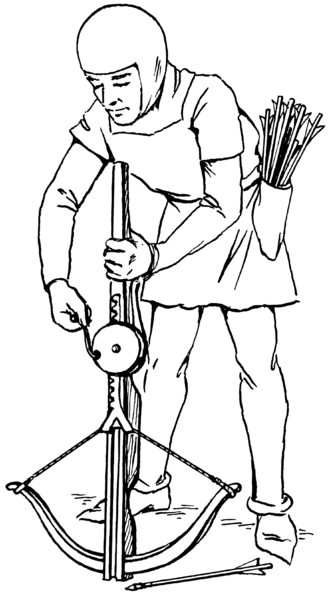
The crossbow is handheld in a similar fashion to the stock of a long gun. It didn’t take a lot of skill to use a crossbow; especially in comparison to the years of training required for the longbow. Because of this, many young boys and injured soldiers used crossbows. This was generally seen as an issue: An untrained person could easily injure a knight in plate mail with this weapon.
Crossbows use a locking mechanism to maintain draw. The shooter only needs to pull the string into lock and then release the shot by pressing a lever or trigger. A crossbowman would average two or three shots per minute with a range of 320 to 360 meters. An archer, on the other hand, could shoot ten to twelve with a longbow. While slow and heavy to carry, the crossbow was still a very valuable weapon in the battlefield.













































