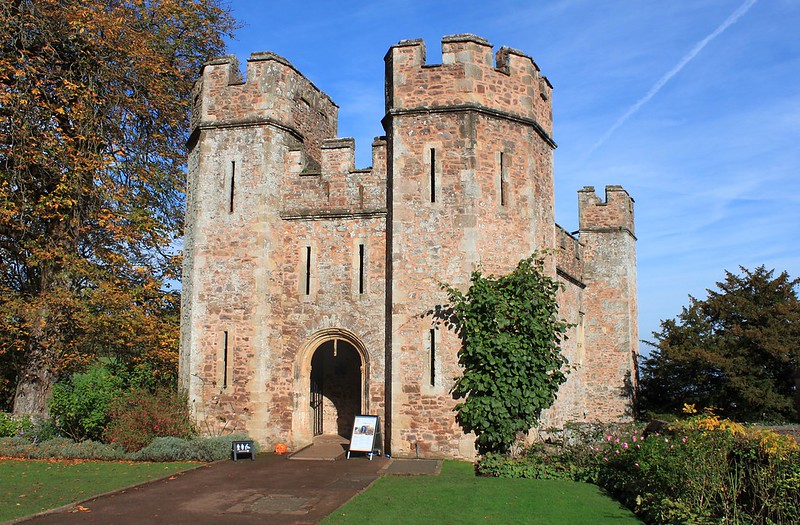
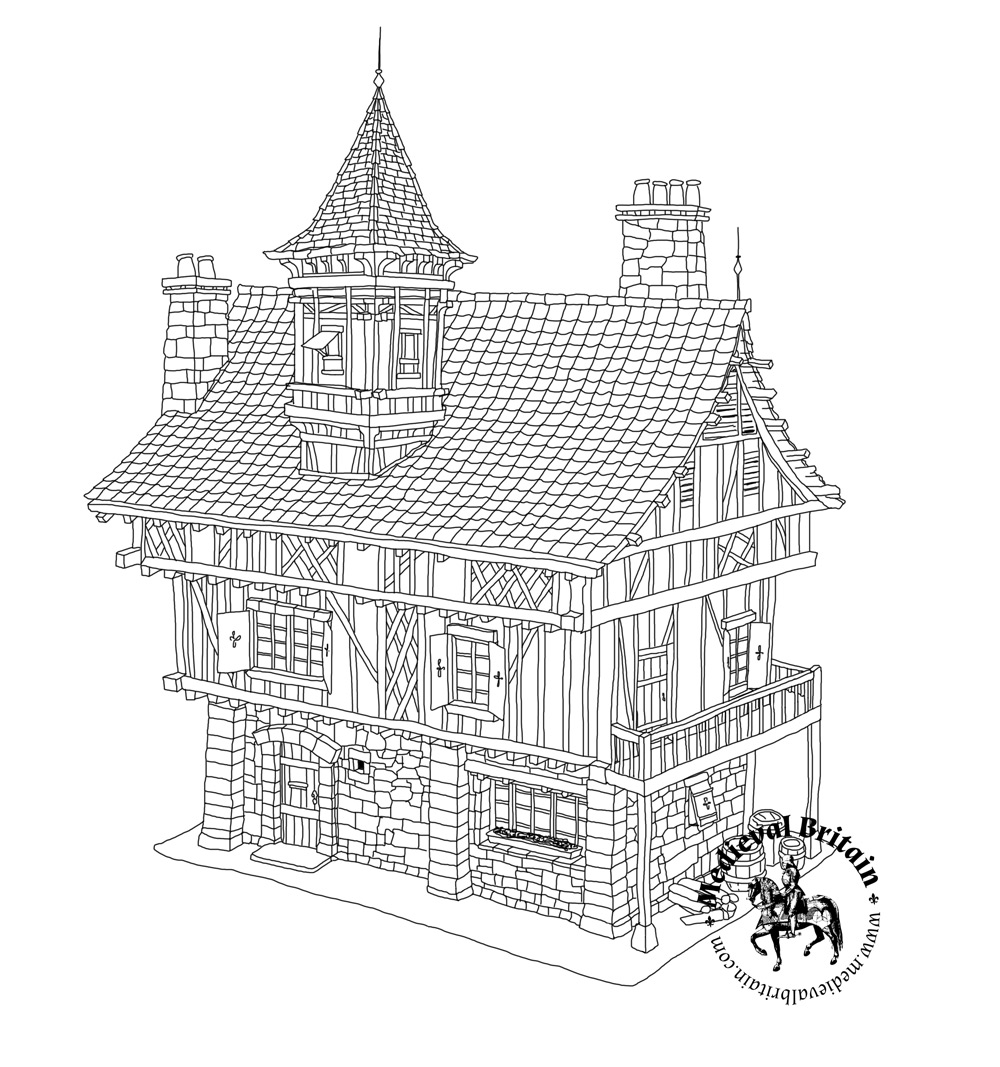
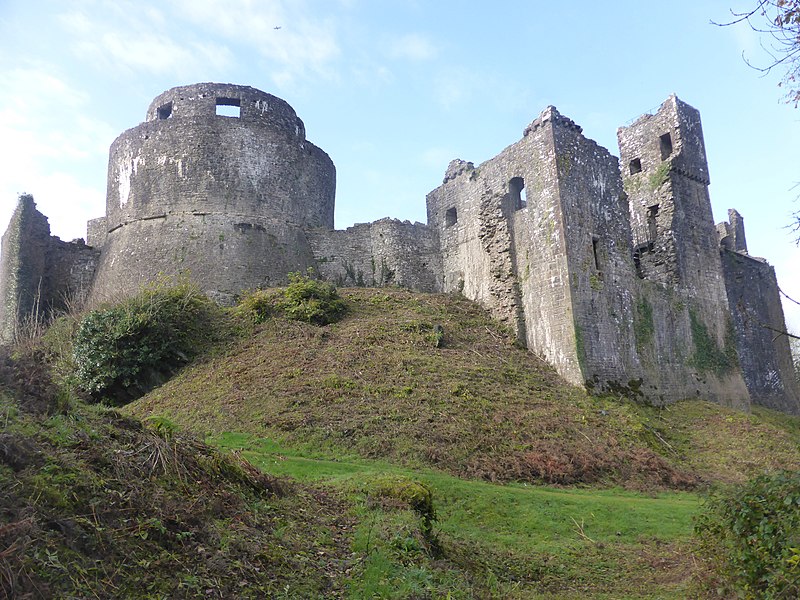
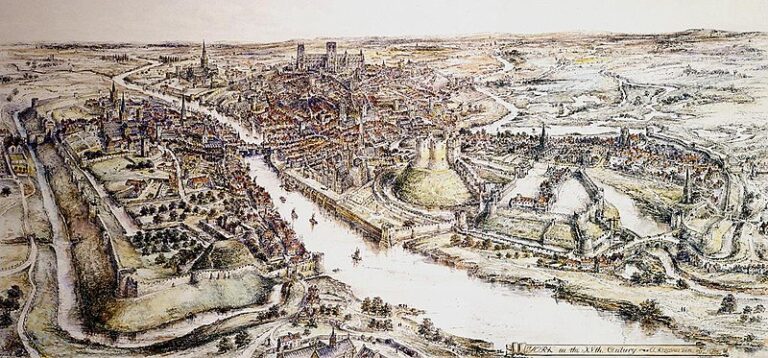
A Motte-and-Bailey Castle is a type of medieval fortification that was commonly used throughout Europe, particularly during the early medieval period. The design consists of two main elements: a raised earthwork called the motte and an enclosed courtyard known as the bailey.
The motte-and-bailey castle, with its simple yet effective design, played a crucial role in medieval military architecture and the defense of territories during a time of political instability and conflict.
The Motte
The motte is a raised mound of earth, often artificial, that typically supports a wooden or stone tower. This elevated position provided a strategic advantage, offering a better vantage point for observation and defense. The motte was sometimes surrounded by a defensive palisade or wall.
The Bailey
The bailey is a courtyard or open space enclosed by a protective ditch and a palisade or wall. It is located at the base of the motte and served various functions, such as providing space for additional buildings, housing troops, and acting as a living area for the castle’s inhabitants.
Key Features of a Motte-and-Bailey Castle
Drawbridge or Causeway: Access to the motte from the bailey was often facilitated by a drawbridge or causeway, adding an extra layer of defense.
Palisade or Wall: Both the motte and the bailey were usually surrounded by a defensive barrier, initially made of wood and later replaced by stone in more permanent structures.
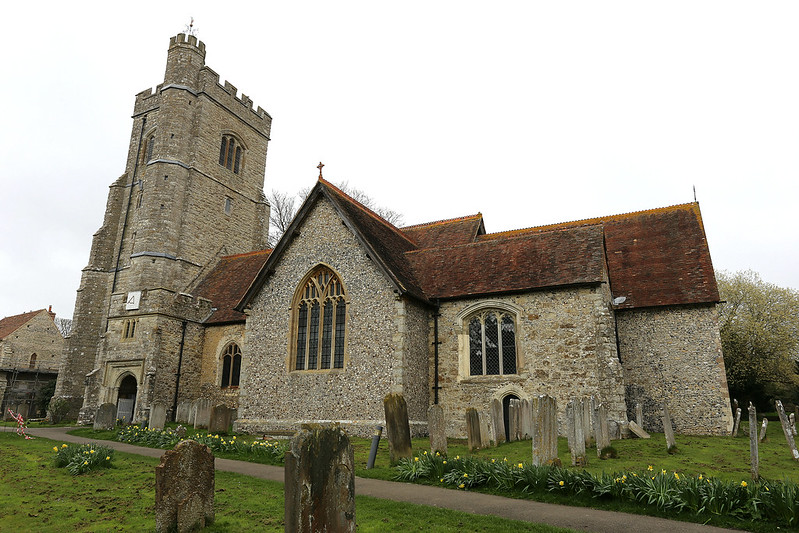
Tower or Keep: The tower or keep on the motte served as the primary residence for the castle’s lord and as a last line of defense. Over time, some motte-and-bailey castles evolved into more elaborate stone structures.
Rapid Construction
One fascinating aspect of motte-and-bailey castles is their speed of construction. The earthworks and wooden structures could be built relatively quickly, allowing for the establishment of fortified positions in a short period. This adaptability made them valuable for military leaders responding to shifting circumstances.
Purpose and Evolution of the Motte-and-Bailey Castle
Defensive Strategy: The design of the motte-and-bailey castle was strategic, offering a combination of elevation, a defensible structure, and a secure courtyard. It was a practical solution for providing protection during a tumultuous period in medieval history.
Adaptability: Mottes and baileys were relatively easy and quick to construct, making them adaptable to changing circumstances. They could be built rapidly in new locations or modified to suit evolving military tactics.
Transition to Stone Castles: While motte-and-bailey castles were prevalent in the early medieval period, many were later replaced or evolved into more formidable stone structures as building techniques advanced.
Symbol of Authority
Mottes served not only as defensive structures but also as symbols of authority. The elevated position of the motte, topped with a tower or keep, visually emphasized the power and status of the castle’s lord. The motte often became a focal point of the castle’s design, reflecting the hierarchical structure of medieval society.